
Chapter 1 : Data Handling using Pandas
- Introduction to Pandas
- Data Structure in Pandas
- Introduction to Series
- Creation of Series
- Series Attributes
- Mathematical operations on Series
- Head and Tail Function
- Slicing in Series
- Selection in Series
Data Structures in Pandas
Data Structure is a specific way to organize, manage and store data, so that it can be accessed and modified as per need. Data structure are also helpful in storing large amount of data and allows operations on them , such as searching, inserting, deleting, updating etc.
Data Structures in Pandas
There are two data structures in pandas: Series and DataFrame
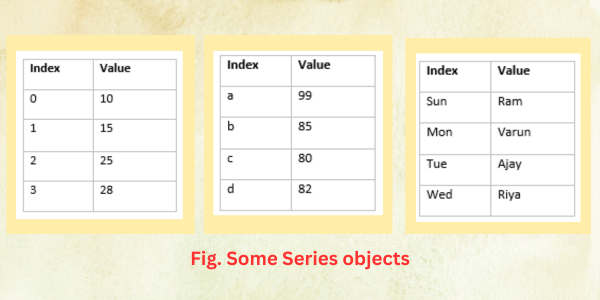
- Series – It is a one dimensional labelled array. A series has two component : one is index and other is its values. Each values have an index value. Some examples of Series are given below:
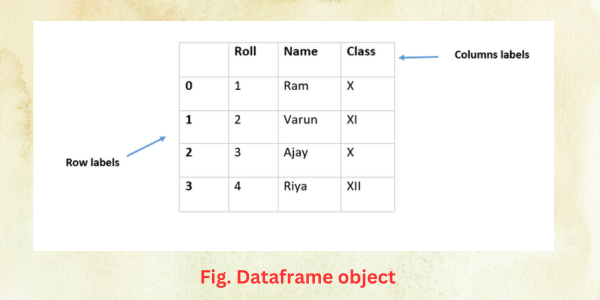
- DataFrame – It is a two dimensional labelled array in which data is arranged in rows and columns. Labels or indexes are used to identify a column or a row.
Difference between Series and DataFrame?
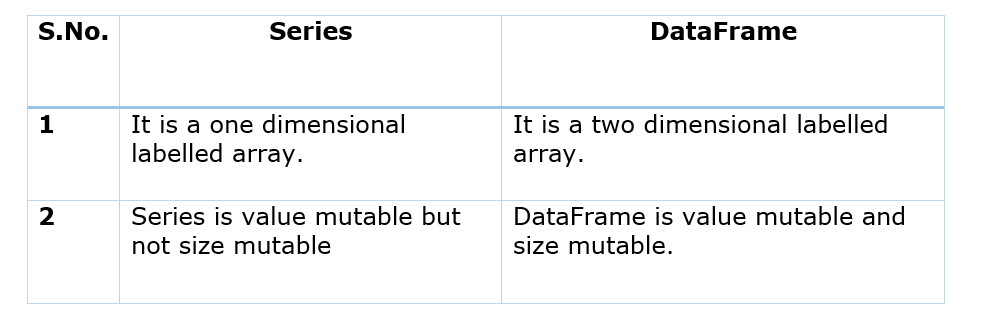
- Here value mutable means that values present in a series or a dataframe can be modified/updated. And size mutable means that more data/rows/columns can be added even after creation of Dataframe.



